Open Access
Yael Strulovici-Barel, Robert J. Kaner & Ronald G. Crystal

Respiratory Research volume 24, Article number: 180 (2023)
Abstract
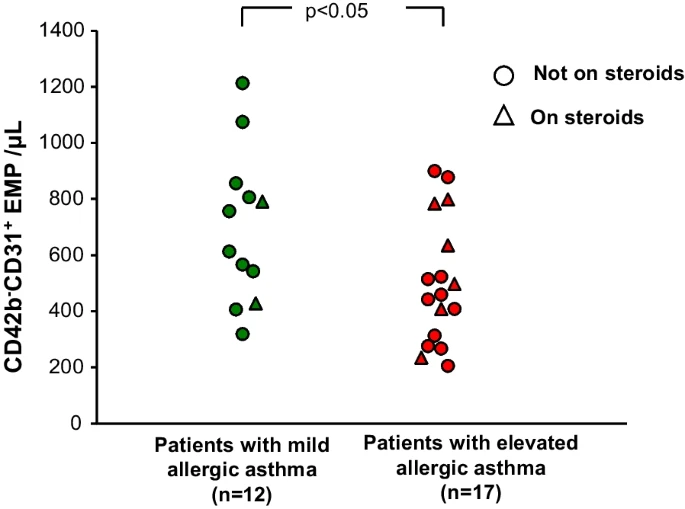
While asthma is considered an inflammatory-mediated airway epithelial and smooth muscle disorder, there is increasing evidence of airway capillary endothelial dysfunction associated with vascular remodelling and angiogenesis in some individuals with this condition. The inflammation is typically characterized as type-2 high (eosinophilic) vs type 2-low (neutrophilic and pauci-granulocytic); we hypothesized that the type-2 high group would be more likely to evidence endothelial dysfunction. As a biomarker of these processes, we hypothesized that nonsmokers with allergic asthma may have elevated plasma levels of endothelial microparticles (EMPs), membrane vesicles that are shed when endothelial cells undergo activation or apoptosis. Total and apoptotic circulating EMPs were measured by fluorescence-activated cell analysis in patients with allergic asthma (n = 29) and control subjects (n = 26), all nonsmokers. When the entire group of patients with asthma were compared to the control subjects, there were no differences in total circulating EMPs nor apoptotic EMPs. However, patients with asthma with elevated levels of IgE and eosinophils had higher levels of apoptotic EMPs, compared to patients with asthma with mildly increased IgE and eosinophil levels. This observation is relevant to precision therapies for asthma and highlights the importance of sub-phenotyping in the condition.