Research – Open Access
Hiroaki Ogata, Katsuyuki Katahira, Aimi Enokizu-Ogawa, Yujiro Jingushi, Akiko Ishimatsu, Kazuhito Taguchi,
Hiroko Nogami, Hiroshi Aso, Atsushi Moriwaki & Makoto Yoshida
BMC Pulmonary Medicine volume 22, Article number: 22 (2022)
Abstract
Background
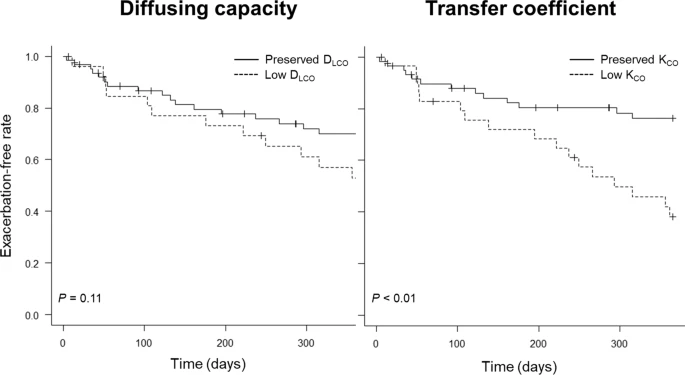
Asthma–chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) overlap (ACO) patients experience exacerbations more frequently than those with asthma or COPD alone. Since low diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO) is known as a strong risk factor for severe exacerbation in COPD, DLCO or a transfer coefficient of the lung for carbon monoxide (KCO) is speculated to also be associated with the risk of exacerbations in ACO.
Methods
This study was conducted as an observational cohort survey at the National Hospital Organization Fukuoka National Hospital. DLCO and KCO were measured in 94 patients aged ≥ 40 years with a confirmed diagnosis of ACO. Multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for the exacerbation-free rate over one year were estimated and compared across the levels of DLCO and KCO.
Results
Within one year, 33.3% of the cohort experienced exacerbations. After adjustment for potential confounders, low KCO (< 80% per predicted) was positively associated with the incidence of exacerbation (multivariable-adjusted HR = 3.71 (95% confidence interval 1.32–10.4)). The association between low DLCO (< 80% per predicted) and exacerbations showed similar trends, although it failed to reach statistical significance (multivariable-adjusted HR = 1.31 (95% confidence interval 0.55–3.11)).
Conclusions
Low KCO was a significant risk factor for exacerbations among patients with ACO. Clinicians should be aware that ACO patients with impaired KCO are at increased risk of exacerbations and that careful management in such a population is mandatory.
