Kelly A, Lavender P. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024 Mar;16(2):130-141. https://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2024.16.2.130
Abstract
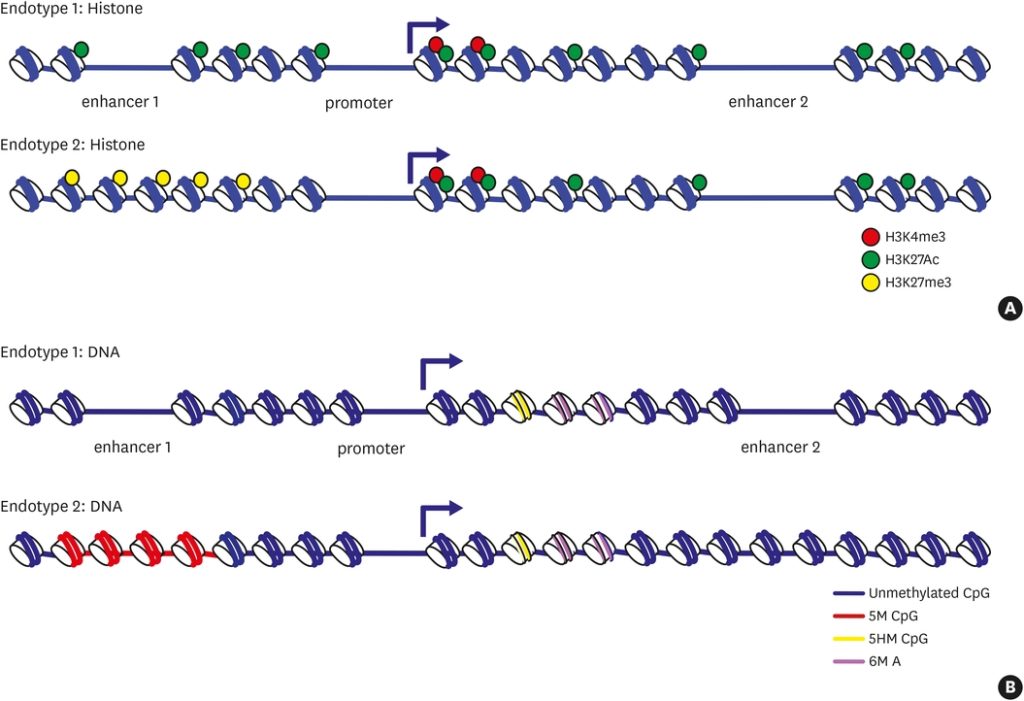
The prevalence of asthma escalated rapidly in the late 20th century. In 2019, the World Health Organization estimated the global number of people affected by the condition to be approximately 260 million, causing 450,000 deaths during that year. While there have been advances in therapeutics with the emergence of biologics targeting T2-high asthma, there is still little clarity on the mechanisms underlying the origins of both the condition and all of its endotypes. Several biomarkers for particular asthma phenotypes have been documented. These are generally identified from transcriptomics and proteomics protocols and tend to be biased to T2-high phenotypes. In this review, we summarize some suggestions that analysis of epigenomes may provide alternative datasets that inform of broader asthma endotypes and might highlight pathways amenable for therapeutic intervention.
