Yao, Tsung-Chieh et al. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice. Articles in Press October 03, 2024 Open access
ABSTRACT
BACKGROUND
Leukotriene-receptor antagonists (LTRA) and inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are common controller medications for asthma, but limited studies examine their comparative risks on neuropsychiatric adverse events (NAEs) in asthma patients.
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the comparative risks of LTRA versus ICS on seven distinct categories of NAEs in asthma patients at a nationwide level.
METHODS
We conducted a nationwide cohort study during 2010-2021. Incident NAEs and its clinical subgroups (e.g., psychotic disorders, anxiety disorders, movement disorders, behavioral and emotional disorders, mood disorders, sleep-related disorders, and personality disorders) were assessed. Cox proportional hazards regressions were employed to quantify the comparative risks.
RESULTS
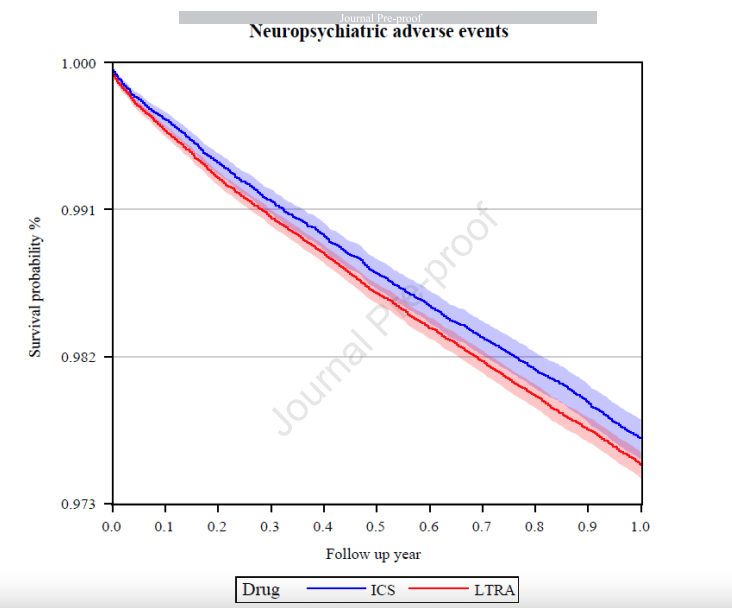
There were 1,249,897 asthma patients aged 6-64 years. Incidence rates for NAEs were 25.10 per 1000 person-years among patients treated with LTRA, and 23.46 per 1000 person-years among those treated with ICS. The incidence rate difference was 1.64 [95%CI: 0.30-2.98] per 1000 person-years. Positive associations of NAEs and three clinical subgroups were found in patients treated with LTRA compared to ICS (hazard ratios (HR): 1.06 [95%CI: 1.00-1.12] for NAEs; HR: 1.88 [95%CI: 1.24-2.84] for psychotic disorders; HR: 1.10 [95%CI: 1.01-1.20] for anxiety disorders; and HR: 1.27 [95%CI: 1.02-1.58] for behavioral and emotional disorders), but not for movement disorders, mood disorders, sleep-related disorders, and personality disorders.
CONCLUSIONS
This nationwide cohort study identified heightened risks, ranging from 6% to 88%, of NAEs and three clinical subgroups in asthma patients treated with LTRA compared to ICS. These findings underscore the necessity for clinicians to communicate with patients regarding potential neuropsychiatric harms when prescribing LTRA.
