Liu, Tt., Zhang, Z., Deng, J. et al. Cell Death Discov. 11, 90 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-025-02371-6
Abstract
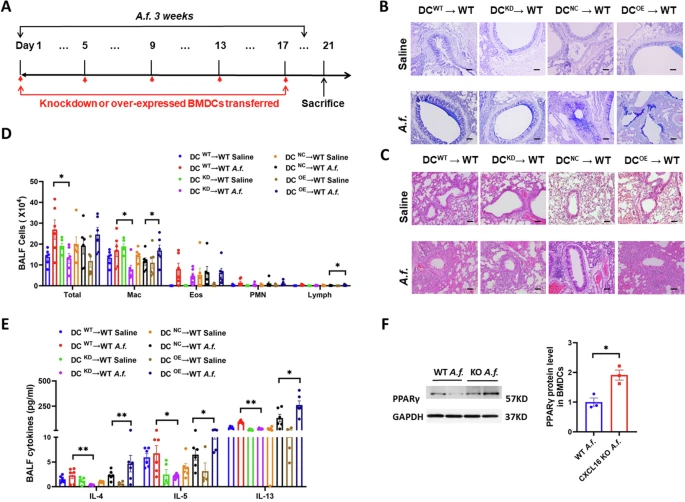
The inflammatory microenvironment influences dendritic cell-mediated antigen presentation to regulate asthma Th2 inflammation. The scavenger receptor is expressed on DCs and regulates antigen presentation and T priming. However, whether the transmembrane scavenger receptor (SR-PSOX/CXCL16) regulates the phenotype and antigen presentation function of DCs remains unclear. We found that CXCL16 is mainly expressed on DCs in the lung tissues of asthma patients and asthma mice. CXCL16 knockout led to the suppression of airway inflammation, mucus overproduction, and airway hyperresponsiveness in Aspergillus-induced asthma. In addition, the adoptive transfer of Aspergillus-pulsed DCs shows the CXCL16+ DCs exerted a promoting role in airway inflammation, the CXCL16− DCs inhibit airway inflammation. Additionally, RNA sequencing and flow cytometry data revealed that CXCL16 knockout inhibits airway inflammation by suppressing the antigen processing and presentation function of DCs, which was mediated by MHC II chaperone H2-DM. Furthermore, we found CXCL16 knockout suppressed dendritic cells differentiated forward to cDC2b subtype which is mainly charged with antigen presentation to T cell. In conclusion, we found that CXCL16 downregulated the capacity of DC antigen processing and presentation to suppress airway inflammation by reducing H2-DM expression which mediated DC differentiation. The study suggested that inhibition of CXCL16 can be a potential therapy for asthma.
