- Research
- Open Access
Zhongping Wu, Ruibo Huang, Liping Zhong, Yi Gao & Jinping Zheng
BMC Pulmonary Medicine volume 22, Article number: 23 (2022)
Abstract
Background
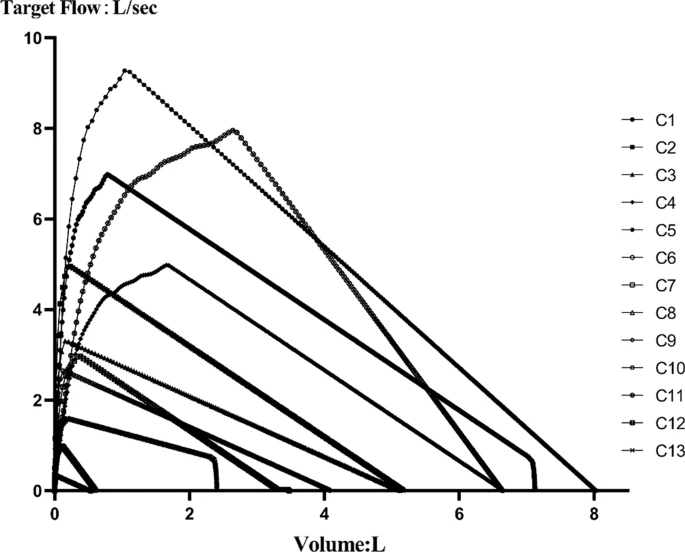
The spirometer is an important element in lung function examinations, and its accuracy is directly related to the accuracy of the results of these examinations and to the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Our aim was to conduct a performance analysis of the detection techniques of differential pressure and ultrasonic portable spirometers commonly used in China.
Methods
A standard flow/volume simulator was used to analyze the performance (accuracy, repeatability, linearity, impedance, and so on) of portable spirometers, 4 imported and 6 domestic, based on 13 curves generated by different air sources in the ISO 26782:2009 standard. A Bland–Altman diagram was used to evaluate the consistency between the values measured by the spirometers and the simulator.
Results
The pass rates for accuracy, repeatability, linearity, and impedance for the 10 different portable spirometers were 50%, 100%, 70%, and 70%, respectively. Only 30% (3/10) of the spirometers—2 domestic and 1 imported—met all standards of quality and performance evaluation, while the rest were partially up to standard. In the consistency evaluation, only 3 spirometers were within both the consistency standard range and the acceptability range.
Conclusion
The quality and performance of different types of portable spirometers commonly used in the clinic differ. The use of a standard flow/volume simulator is helpful for the standard evaluation of the technical performance of spirometers.
